Could you imagine a world without sound? Do you ever buy a phone or laptop without audio? Well, the answer is simple. No one would prefer a device without sounds. It’s not about devices only; any sound system without a speaker is worthless.
A speaker is the most basic part of the audio system. It enables you to listen to any voices, music, and other sounds. Have you ever wondered how speakers work? Well, I do. That’s why I learned and experimented more about speakers. And now, I understand the analogy of speakers.
Do you want to know how speakers produce sounds? Let’s deep dive into our ultimate Speaker working guide and explore more about speakers:
How do Speakers Work?
The first speaker was invented in 1876 by Graham Bel. However, the world is developing quickly, and we observe innovative gadgets. However, the basic principle of the speaker is still the same. The technology may vary for different companies, but the overall working is the same.
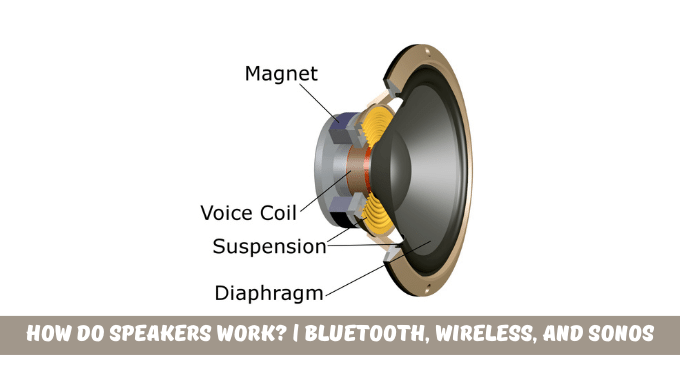
Now the question is, how do speakers work? A speaker works by converting an electrical signal into mechanical signal. To be clearer, a speaker takes an audio signal (input) and passes it through a coil in a magnetic field. Then, compressing it into the sound signal (output).
Parts of Speaker
Before discussing speakers’ working, let’s have a quick view of its main parts:
- A driver converts the electric energy of audio signals into mechanical by pushing air molecules.
- A diaphragm for making sound waves from sound signals.
- A cone of larger size is used for maximum air movement.
- Magnet to use as a converter for negative and positive air pressure.
- Voice coil provides the necessary electromagnetic force.
Structure of Speaker
Let’s explore and understand more about the speaker’s analogy:
Outer Box
A speaker works by converting signals and producing negative and positive pressure on waves. So, it is mounted in a closed box to avoid air disturbance and properly assemble audio signals.
Any type of closed box provides the same balanced sound effect. But if you try to use a speaker’s setup in an open container, it can cause sound distortion and imbalance.
Tweeters and Woofers
Speakers have tweeters, woofers, or both in the front of their box. A Large woofer provides a louder and clearer sound. A speaker may have more than one subwoofer. This is because different restrictions on single tweeters lower the sound quality.
So, multiple woofers are used to enhance sound effects. In the case of multiple tweeters. Each one is assigned a different frequency range.
Back Knobs
A speaker has several knobs, ports, and buttons on the backside. Some are used for device connection, charging connections, and other purposes. Similarly, the buttons are used for sound, bass, intensity, and frequency adjustments.
Working of Wireless and Bluetooth Speakers
In recent years, the world has witnessed a 360° shift technical shift. And now, with innovation, we have switched from normal cable speakers to wireless and Bluetooth speakers. Although they have the same working principle with a slight technical difference.
Let’s get straight into the workings of wireless and Bluetooth speakers:
How do Bluetooth Speakers Work?
Bluetooth and Wi-Fi have become the most innovative and useable technologies. A Bluetooth speaker works by receiving and delivering digital signals. Bluetooth speakers have built-in amplifiers. They can catch and convert the audio signals directly without any cable. Such transmission is called digital transmission of signals.
It works by connecting a device having Bluetooth with your speaker. Both devices approve pairing with each other. Then, via Bluetooth transmission, digital signals are transferred to the speaker. You can convert, amplify, transmit, and receive the audio like normal speakers.
Bluetooth speakers are widely used in homes, offices, pubs, small gatherings, golf courts, and hotels.
How do Wireless Speakers Work?
With the growing technology, we are switching to more convenient gadgets. So, a wireless speaker is more preferred than a cable speaker. The biggest flex of wireless speakers is their portability. They are also compact, lightweight, and have more innovative features.
Wireless speakers have two working technologies. It can either work as a Bluetooth speaker or as a Wi-Fi speaker. We have discussed the working of Bluetooth speakers.
In the case of a Wi-Fi speaker, you have to connect the wireless speaker with your Wi-Fi connection. These speakers are Spotify, Google Assistant, and other smart apps compatible. You can listen to your favorite music and podcasts via wireless speakers.
How do Sonos Speakers Work?
Sonos is one of the most prominent companies in the audio industry. The company offers a wide range of speakers. All the products from Sonos are well, compact, and portable with cool appearance and modern features.
Sonos speakers work just like wireless Bluetooth or Wi-Fi speakers. They have more than 100 music streaming services. You can connect a Sonos speaker with your device or Wi-Fi connection and enjoy any music, movies, podcasts, shows, and much more.
Sonos speakers are compatible with Apple music streaming, Spotify, Pandora, Amazon, Google Music, and other streaming services. Sonos speakers work in the same way as other wireless speakers.
Some Top Companies to Buy Wireless or Bluetooth Speakers
A lot of companies are offering incredible wireless speakers with exceptional features. Here is the list of our top picks to consider before buying a Bluetooth speaker:
- Sonos
- JBL
- Ultimate Ear
- Sony SRS series
- Anker Soundcore
- Amazon Gen series
- Marshall
What distinguishes an effective speaker from a poor one?
The best way to test the sound quality of speakers is to compare how closely the waveform or pressure wave in the air resembles the electronic wave or audio recording that has passed through the system amplifier. The frequencies are reproduced so the listener can hear them and judge whether they sound accurate or unchanged.
The speaker is probably very good if the frequency accuracy is high and does not change details. In contrast, low-frequency accuracy with some audible information change can indicate poorer audio quality. For a great option of speakers, soundcore 3 offers exceptional value for money.
Several variables are taken into consideration when testing speakers to determine the audio accuracy and overall listening experience. These speaker-related variables include information about the frequency response, distortion, and audio dispersion. Frequency response is the most crucial and has the biggest impact on the audio of all the determining factors.
Why understanding speaker operation is valuable:
To enjoy speakers and listen to them, you do not need to understand the science behind them. However, if you plan to spend a lot of money on audio equipment, it is always a good idea to first educate yourself. You can recognize snake oil salesmen by understanding why certain design decisions were made, how they affect the sound, and why they were made.
Understanding how speakers function can also aid in problem diagnosis. If this article has piqued your interest and you would like to learn more, you can find a wealth of online resources that will teach you how to construct them from parts that are easily accessible.
Conclusion
The desire to understand how speakers work does not have to be suppressed by the intimidating science of speakers; instead, it can be made simple by a concise breakdown of the process of speakers and how they work.
Finally, learning something new about something so common in everyday life, such as the speaker, is well worth the effort.
FAQs
What is the speed at which a speaker vibrates?
The sound range typically varies from 20Hz to 20 kHz, with many speakers able to vibrate within an audible range with lower bandwidth.
What is the Path of Sound Through a Speaker?
Vibration or movement in the air causes the speaker to produce sound. In addition to air, solids and liquids can also conduct sound, but speakers that we use for listening to music use air as the transmission medium. The air molecules in the vicinity of an object move whenever it vibrates.















Leave a Reply